MEC172xEVB ASSY6906
Overview
The MEC172xEVB_ASSY6906 kit is a future development platform to evaluate the Microchip MEC172X series microcontrollers. This board needs to be mated with part number MEC172x 144WFBGA SOLDER DC ASSY 6914 (cpu board) in order to operate. MEC172x and MEC152x SPI image formats are not compatible with each other.
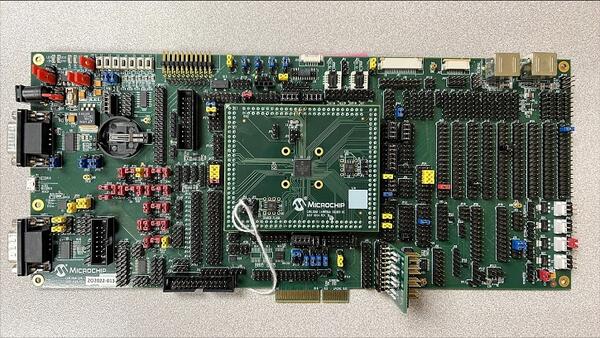
Hardware
MEC172x ARM Cortex-M4 Processor
416 KB RAM and 128 KB boot ROM
Keyboard interface
ADC & GPIO headers
UART0 and UART1
FAN0, FAN1, FAN2 headers
FAN PWM interface
JTAG/SWD, ETM and MCHP Trace ports
PECI interface 3.0
I2C voltage translator
10 SMBUS headers
VCI interface
1 Hardware Driven PS/2 Port
eSPI header
2 Sockets for SPI NOR chips
One reset and VCC_PWRDGD pushbuttons
One external PCA9555 I/O port with jumper selectable I2C address.
One external LTC2489 delta-sigma ADC with jumper selectable I2C address.
Board power jumper selectable from +5V 2.1mm/5.5mm barrel connector or USB Micro A connector.
For more information about the SOC’s please see MEC172x Reference Manual 1
Supported Features
The mec172xevb_assy6906 board configuration supports the following hardware features:
Interface |
Controller |
Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
NVIC |
on-chip |
nested vector interrupt controller |
SYSTICK |
on-chip |
systick |
UART |
on-chip |
serial port |
GPIO |
on-chip |
gpio |
I2C |
on-chip |
i2c |
PINMUX |
on-chip |
pinmux |
PS/2 |
on-chip |
ps2 |
KSCAN |
on-chip |
kscan |
TACH |
on-chip |
tachometer |
RPMFAN |
on-chip |
Fan speed controller |
Other hardware features are not currently supported by Zephyr.
The default configuration can be found in the boards/arm/mec172xevb_assy6906/mec172xevb_assy6906_defconfig Kconfig file.
Connections and IOs
This evaluation board kit is comprised of the following HW blocks:
MEC172x EVB ASSY 6906 Rev A MEC172x EVB Schematic 2
MEC172x 144WFBGA SOLDER DC ASSY 6914 with MEC172x silicon MEC172x Daughter Card Schematic 3
SPI DONGLE ASSY 6791 SPI Dongle Schematic 4
System Clock
The MEC1723 MCU is configured to use the 96Mhz internal oscillator with the on-chip PLL to generate a resulting EC clock rate of 12 MHz. See Processor clock control register in chapter 4 “4.0 POWER, CLOCKS, and RESETS” of the data sheet in the references at the end of this document.
Serial Port
UART1 is configured for serial logs.
Jumper settings
Please follow the jumper settings below to properly demo this board. Advanced users may deviate from this recommendation.
Jumper setting for MEC172x EVB Assy 6906 Rev A1p0
Boot-ROM Straps
These jumpers configure MEC172x Boot-ROM straps.
JP1 (CR_STRAP) |
JP2 (JTAG_STRAP) |
JP3 (CMP_STRAP) |
JP7 (BSS_STRAP) |
JP160 (UART_BSTRAP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1-2 |
2-3 |
2-3 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
JP7 1-2 pulls SHD SPI CS0# up to VTR2. MEC172x Boot-ROM samples
SHD SPI CS0# and if high, it loads code from SHD SPI.
Peripheral Routing Jumpers
Each column of the following table illustrates how to enable UART0, UART1, SHD SPI and SWD, respectively.
UART0 (P11) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
JP13 |
JP17 |
JP19 |
JP22 |
JP88 |
JP89 |
JP93 |
2-3 |
2-3 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
2-3 |
2-3 |
1-3 |
5-6 |
5-6 |
4-5 |
4-5 |
2-4 |
||
8-9 |
8-9 |
|||||
11-12 |
11-12 |
|||||
14-15 |
14-15 |
|||||
17-18 |
17-18 |
|||||
20-21 |
||||||
23-24 |
||||||
UART1 |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(P12) |
(P2) |
||||||||||||
JP11 |
JP14 |
JP19 |
JP24 |
JP90 |
JP94 |
JP157 |
JP11 |
JP19 |
JP24 |
JP90 |
JP94 |
JP157 |
|
1-2 |
1-2 |
20-21 |
2-3 |
2-3 |
1-3 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
11-12 |
5-6 |
2-3 |
1-3 |
1-3 |
|
4-5 |
5-6 |
2-4 |
4-5 |
4-5 |
8-9 |
2-4 |
4-6 |
||||||
8-9 |
8-9 |
7-8 |
17-18 |
7-9 |
|||||||||
11-12 |
10-11 |
23-24 |
10-12 |
||||||||||
14-15 |
|||||||||||||
17-18 |
|||||||||||||
NOTE: The “Hello World” example outputs at UART1 P12 .
SHD_SPI |
SWD |
LED4-5 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
JP23 |
JP25 |
JP156 |
J18 |
JP21 |
2-3 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
8-9 |
4-5 |
8-9 |
11-12 |
16-17 |
||
14-15 |
||||
17-18 |
||||
Jumper settings for MEC172x 144WFBGA Socket DC Assy 6914 Rev A0p1
The jumper configuration explained above covers the base board. The ASSY
6914 MEC172x CPU board provides capability for an optional, external 32KHz
clock source. The card includes a 32KHz crystal oscillator. The card can
also be configured to use an external 50% duty cycle 32KHz source on the
XTAL2/32KHZ_IN pin. Note, firmware must set the MEC172x clock enable
register to select the external source matching the jumper settings. If
using the MEC172x internal silicon oscillator then the 32K jumper settings
are don’t cares. JP1 on DC is for scoping test clock outputs. Please
refer to the schematic in reference section below.
Parallel 32KHz crystal configuration
JP1 |
JP2 |
|---|---|
1-2 |
2-3 |
External 32KHz 50% duty cycle configuration
JP2 |
JP3 |
|---|---|
NC |
1-2 |
NOTE: JP121 3-4 on base board also needs to be loaded.
Programming and Debugging
Setup
If you use Dediprog SF100 programmer, then setup it.
Windows version can be found at the SF100 Product page 7.
Linux version source code can be found at SF100 Linux GitHub 6. Follow the SF100 Linux manual 8 to complete setup of the SF100 programmer. For Linux please make sure that you copied
60-dediprog.rulesfrom theSF100Linuxfolder to the/etc/udev/rules.s(or rules.d) then restart service using:$ udevadm control --reload
Add directory with program
dpcmd(on Linux) ordpcmd.exe(on Windows) to yourPATH.Clone the MEC172x SPI Image Gen 5 repository or download the files within that directory.
Make the image generation available for Zephyr, by making the tool searchable by path, or by setting an environment variable
MEC172X_SPI_GEN, for example:export MEC172X_SPI_GEN=<path to tool>/mec172x_spi_gen_lin_x86_64Note that the tools for Linux and Windows have different file names.
The default MEC172X_SPI_CFG file is spi_cfg.txt located in ${BOARD_DIR}/support. If needed, a custom SPI image configuration file can be specified to override the default one.
export MEC172X_SPI_CFG=custom_spi_cfg.txt
Wiring
Connect the SPI Dongle ASSY 6791 to
J34in the EVB.
Connect programmer to the header J6 on the Assy6791 board, it will flash the SPI NOR chip
U3. Make sure that your programmer’s offset is 0x0. For programming you can use Dediprog SF100 or a similar tool for flashing SPI chips.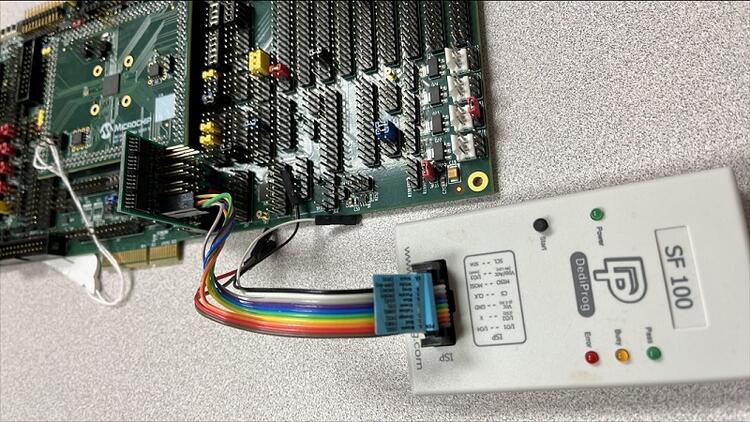
Note
Remember that SPI MISO/MOSI are swapped on Dediprog headers! Use separate wires to connect Dediprog pins with pins on the Assy6791 SPI board. Wiring connection is described in the table below.
Dediprog Connector
Assy6791 J6 Connector
VCC
1
GND
2
CS
3
CLK
4
MISO
6
MOSI
5
Connect UART1 port of the MEC17xxEVB_ASSY_6906 board to your host computer using the RS232 cable.
Apply power to the board via a micro-USB cable. Configure this option by using a jumper between
JP30 7-8.
Building
Build Hello World application as you would normally do.
The file
spi_image.binwill be created if the build system can find the image generation tool. This binary image can be used to flash the SPI chip.
Flashing
Run your favorite terminal program to listen for output. Under Linux the terminal should be
/dev/ttyUSB0. Do not close it.For example:
$ minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB0 -o
The -o option tells minicom not to send the modem initialization string. Connection should be configured as follows:
Speed: 115200
Data: 8 bits
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flash your board using
westfrom the second terminal window. Split first and second terminal windows to view both of them.$ west flash
Note
When west process started press Reset button
S2and do not release it till the whole west process will not be finished successfully.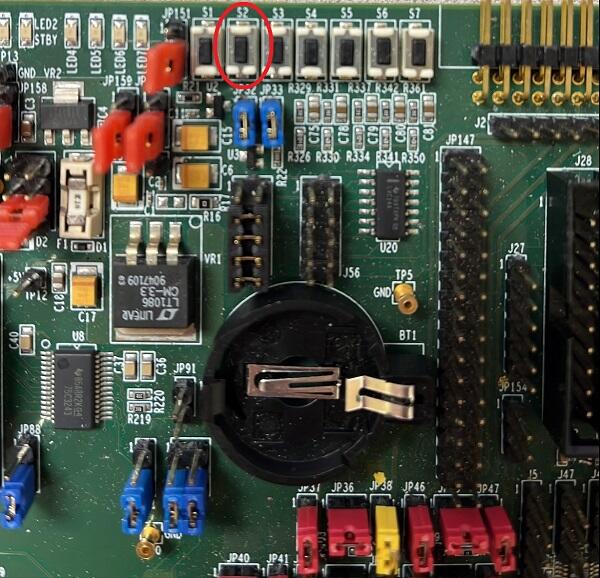
Note
If you don’t want to press Reset button every time, you can disconnect SPI Dongle ASSY 6791 from the EVB during the west flash programming. Then connect it back to the
J34header and apply power to the EVB. Result will be the same.You should see
"Hello World! mec172xevb_assy6906"in the first terminal window. If you don’t see this message, press the Reset button and the message should appear.
Debugging
This board comes with a Cortex ETM port which facilitates tracing and debugging using a single physical connection. In addition, it comes with sockets for JTAG only sessions.
Troubleshooting
In case you don’t see your application running, please make sure
LED1andLED2are lit. If one of these is off, then check the power-related jumpers again.If you can’t program the board using Dediprog, disconnect the Assy6791 from the main board Assy6906 and try again.
If Dediprog can’t detect the onboard flash, press the board’s Reset button and try again.
PCA9555 Enabling
To enable PCA9555PW and test the I2C on mec172xevb_assy6906, additional works are needed:
As the I2C slave device NXP pca95xx on mec172xevb_assy6906 is connected to I2C00 port, however, I2C00 port is shared with UART2 RS232 to TTL converter used to catch serial log, so it’s not possible to use UART2 and I2C00 port simultaneously. We need to change to use I2C01 port by making some jumpers setting as below:
Pin 1
Pin 2
Comment
JP49.1
JP49.2
Connect PCA9555 VCC to +3.3V_STBY
JP53.1
JP53.2
Select address 0100b, which means 0x26
JP12.13
JP12.14
Connect I2C01_SDA from CPU to header J20
JP12.4
JP12.5
Connect I2C01_SCL from CPU to header J20
JP77.7
JP77.8
External pull-up for I2C01_SDA
JP77.9
JP77.10
External pull-up for I2C01_SCL
JP58.1
JP20.1
Connect NXP PCA9555 SCL to I2C01
JP58.3
JP20.3
Connect NXP PCA9555 SDA to I2C01
