u-blox EVK-NINA-B3
Overview
The u-blox EVK-NINA-B30 Development Kit hardware provides support for the u-blox NINA-B30x Bluetooth 5.0 module, based on the Nordic Semiconductor nRF52840 ARM Cortex-M4F CPU and the following devices:
ADC
CLOCK
FLASH
GPIO
I2C
MPU
NVIC
PWM
RADIO (Bluetooth Low Energy and 802.15.4)
RTC
Segger RTT (RTT Console)
SPI
UART
USB
WDT
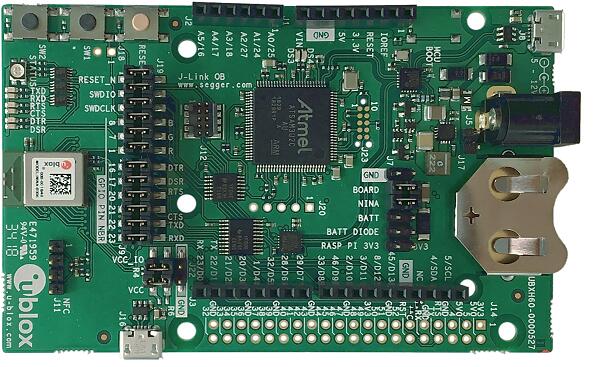
Fig. 215 EVK-NINA-B3 (Credit: u-blox AG)
More information about the EVK-NINA-B3 and the NINA-B30x modules can be found at the u-blox website [1].
Hardware
The NINA-B30x on the EVK-NINA-B30x contains an internal high-frequency oscillator at 32MHz as well as a low frequency (slow) oscillator of 32.768kHz.
Supported Features
The ubx_evkninab3_nrf52840 board configuration supports the following hardware features:
Interface |
Controller |
Driver/Component |
|---|---|---|
ADC |
on-chip |
adc |
CLOCK |
on-chip |
clock_control |
FLASH |
on-chip |
flash |
GPIO |
on-chip |
gpio |
I2C(M) |
on-chip |
i2c |
MPU |
on-chip |
arch/arm |
NVIC |
on-chip |
arch/arm |
PWM |
on-chip |
pwm |
RADIO |
on-chip |
Bluetooth, IEEE 802.15.4 |
RTC |
on-chip |
system clock |
RTT |
Segger |
console |
SPI(M/S) |
on-chip |
spi |
UART |
on-chip |
serial |
USB |
on-chip |
usb |
WDT |
on-chip |
watchdog |
Other hardware features have not been enabled yet for this board. See the u-blox website [1] for a complete list of EVK-NINA-B30x hardware features.
Connections and IOs
LED
LED0 (red) = P0.13
LED1 (green) = P0.25
LED2 (blue) = P1.00
External Connectors
Note
The pin numbers noted below are referenced to the pin 1 markings on the EVK-NINA-B30x for each header
Arduino Headers
Power (J1)
PIN # |
Signal Name |
NINA-B30x Functions |
|---|---|---|
1 |
N/C |
N/A |
2 |
VDD_IO |
N/A |
3 |
RESET |
P0.18 / RESET |
4 |
3V3 |
N/A |
5 |
5V0 |
N/A |
6 |
GND |
N/A |
7 |
GND |
N/A |
8 |
VIN |
N/A |
Analog in (J2)
PIN # |
Signal Name |
NINA-B30x Functions |
|---|---|---|
1 |
A0 |
P0.04 / AIN2 |
2 |
A1 |
P0.30 / AIN6 |
3 |
A2 |
P0.05 / AIN3 |
4 |
A3 |
P0.02 / AIN0 |
5 |
A4 |
P0.28 / AIN4 |
6 |
A5 |
P0.03 / AIN1 |
Digital I/O (J3)
PIN # |
Signal Name |
NINA-B30x Functions |
|---|---|---|
8 |
D7 |
P0.10 |
7 |
D6 |
P0.09 |
6 |
D5 |
P0.11 |
5 |
D4 |
P0.13 |
4 |
D3 |
P0.31 |
3 |
D2 |
P1.12 |
2 |
D1 (TX) |
P1.13 |
1 |
D0 (RX) |
P0.29 |
Digital I/O (J4)
PIN # |
Signal Name |
NINA-B30x Functions |
|---|---|---|
10 |
SCL |
P0.24 |
9 |
SDA |
P0.16 |
8 |
N/C |
N/A |
7 |
GND |
N/A |
6 |
D13 (SCK) |
P0.07 |
5 |
D12 (MISO) |
P1.00 |
4 |
D11 (MOSI) |
P0.15 |
3 |
D10 (SS) |
P0.14 |
2 |
D9 |
P0.12 |
1 |
D8 |
P1.09 |
Programming and Debugging
Applications for the ubx_evkninab3_nrf52840 board configuration can be
built and flashed in the usual way (see Building an Application
and Run an Application for more details); however, the standard
debugging targets are not currently available.
Flashing
Follow the instructions in the Nordic nRF5x Segger J-Link page to install and configure all the necessary software. Further information can be found in Flashing. Then build and flash applications as usual (see Building an Application and Run an Application for more details).
Here is an example for the Hello World application.
First, run your favorite terminal program to listen for output.
$ minicom -D <tty_device> -b 115200
Replace <tty_device> with the port where the EVK-NINA-B30x
can be found. For example, under Linux, /dev/ttyACM0.
Then build and flash the application in the usual way.
# From the root of the zephyr repository
west build -b ubx_evkninab3_nrf52840 samples/hello_world
west flash
Debugging
Refer to the Nordic nRF5x Segger J-Link page to learn about debugging u-blox boards with a Segger J-LINK-OB IC.
Using UART1
The following approach can be used when an application needs to use more than one UART for connecting peripheral devices:
Add device tree overlay file to the main directory of your application:
&pinctrl { uart1_default: uart1_default { group1 { psels = <NRF_PSEL(UART_TX, 0, 14)>, <NRF_PSEL(UART_RX, 0, 16)>; }; }; /* required if CONFIG_PM_DEVICE=y */ uart1_sleep: uart1_sleep { group1 { psels = <NRF_PSEL(UART_TX, 0, 14)>, <NRF_PSEL(UART_RX, 0, 16)>; low-power-enable; }; }; }; &uart1 { compatible = "nordic,nrf-uarte"; current-speed = <115200>; status = "okay"; pinctrl-0 = <&uart1_default>; pinctrl-1 = <&uart1_sleep>; pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; };
In the overlay file above, pin P0.16 is used for RX and P0.14 is used for TX
Use the UART1 as
DEVICE_DT_GET(DT_NODELABEL(uart1))
Overlay file naming
The file has to be named <board>.overlay and placed in the app main directory to be
picked up automatically by the device tree compiler.
Selecting the pins
Pins can be configured in the board pinctrl file. To see the available mappings, open the data sheet for the NINA-B3 at u-blox website [1], Section 3 ‘Pin definition’. In the table 7 select the pins marked ‘GPIO_xx’. Note that pins marked as ‘Radio sensitive pin’ can only be used in under-10KHz applications. They are not suitable for 115200 speed of UART.
