Thingy:53: Matter weather station¶
This Matter weather station application demonstrates the usage of the Matter application layer to build a weather station device. Such a device lets you remotely gather different kinds of data using the device sensors, such as temperature, air pressure, and relative humidity. The device works as a Matter accessory device, meaning it can be paired and controlled remotely over a Matter network built on top of a low-power, 802.15.4 Thread network. You can use this application as a reference for creating your own application.
Note
The Matter protocol is in an early development stage and must be treated as an experimental feature.
Requirements¶
The application supports the following development kits:
Hardware platforms |
PCA |
Board name |
Build target |
|---|---|---|---|
Thingy:53 |
PCA20053 |
|
To commission the weather station device and control it remotely through a Thread network, you also need a Matter controller device configured on PC or smartphone (which requires additional hardware depending on which setup you choose). The recommended way of getting measurement values is using the mobile Matter controller application that comes with a neat graphical interface, performs measurements automatically and visualizes the data.
To program a Thingy:53 device where the preprogrammed MCUboot bootloader has been erased, you need the external J-Link programmer. If you own an nRF5340 DK that has an onboard J-Link programmer, you can also use it for this purpose.
If the Thingy:53 is programmed with Thingy:53-compatible sample or application, then you can also update the firmware using MCUboot’s serial recovery or DFU over Bluetooth LE. See Thingy:53 application guide for details.
Note
Matter requires the GN tool. If you are updating from the nRF Connect SDK version earlier than v1.5.0, see the GN installation instructions.
Overview¶
The application uses a single button for controlling the device state. The weather station device is periodically performing temperature, air pressure, and relative humidity measurements. The measurement results are stored in the device memory and can be read using the Matter controller. The controller communicates with the weather station device over the Matter protocol using Zigbee Cluster Library (ZCL). The library describes data measurements within the proper clusters that correspond to the measurement type.
The application uses MCUboot secure bootloader and SMP protocol for performing over-the-air Device Firmware Upgrade using Bluetooth® LE. For information about how to upgrade the device firmware using a PC or a mobile, see the Updating the device firmware section.
Remote testing in a network¶
By default, the Matter accessory device has Thread disabled, and it must be paired with the Matter controller over Bluetooth LE to get configuration from it if you want to use the device within a Thread network. To do this, the device must be made discoverable over Bluetooth LE.
The Bluetooth LE advertising starts automatically upon the device startup, but only for a predefined period of time (15 minutes by default). If the Bluetooth LE advertising times out, you can re-enable it manually using Button 1.
Additionally, the controller must get the commissioning information from the Matter accessory device and provision the device into the network. For details, see the Testing section.
Matter weather station build types¶
The Matter weather station application does not use a single prj.conf file.
Configuration files are provided for different build types and they are located in the configuration/thingy53_nrf5340_cpuapp directory.
Build types enable you to use different sets of configuration options for each board.
You can create several build type .conf files per board and select one of them when building the application.
This means that you do not have to use one prj.conf file for your project and modify it each time to fit your needs.
Before you start testing the application, you can select one of the build types supported by Matter weather station application, depending on the building method. This application supports the following build types:
ZDebug– Debug version of the application - can be used to enable additional features for verifying the application behavior, such as logs or command-line shell.ZRelease– Release version of the application - can be used to enable only the necessary application functionalities to optimize its performance.
Note
Selecting a build type is optional.
The ZDebug build type is used by default if no build type is explicitly selected.
Configuration¶
See Configuring your application for information about how to permanently or temporarily change the configuration.
User interface¶
- LED 1:
Shows the overall state of the device and its connectivity. The following states are possible:
Short flash on (green color, 50 ms on/950 ms off) - The device is in the unprovisioned (unpaired) state and is not advertising over Bluetooth LE.
Short flash on (blue color, 50 ms on/950 ms off) - The device is in the unprovisioned (unpaired) state, but is advertising over Bluetooth LE.
Rapid even flashing (blue color, 100 ms on/100 ms off) - The device is in the unprovisioned state and a commissioning application is connected through Bluetooth LE.
Short flash on (purple color, 50 ms on/950 ms off) - The device is fully provisioned and has Thread enabled.
- Button 1:
Used during the commissioning procedure. Depending on how long you press the button:
If pressed for 6 seconds, it initiates the factory reset of the device. Releasing the button within the 6-second window cancels the factory reset procedure.
If pressed for less than 3 seconds, it starts the NFC tag emulation, enables Bluetooth LE advertising for the predefined period of time (15 minutes by default), and makes the device discoverable over Bluetooth LE.
- USB port:
Used for getting logs from the device or communicating with it through the command-line interface. It is enabled only for the debug configuration of an application. See the Selecting a build type section to learn how to select the debug configuration.
- NFC port with antenna attached:
Used for obtaining the commissioning information from the Matter accessory device to start the commissioning procedure.
Building and running¶
This sample can be found under applications/matter_weather_station in the nRF Connect SDK folder structure.
See Building and programming an application for information about how to build and program the application.
Selecting a build type¶
Before you start testing the application, you can select one of the Matter weather station build types, depending on your building method.
Selecting a build type in SES¶
To select the build type in SEGGER Embedded Studio:
Go to File > Open nRF Connect SDK project, select the current project, and specify the board name and build directory.
Select Extended Settings.
In the Extra CMake Build Options field, specify
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=selected_build_type. For example, forZReleaseset the following value:-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ZRelease.Do not select Clean Build Directory.
Click OK to re-open the project.
Note
You can also specify the build type in the Additional CMake Options field in Tools > Options > nRF Connect. However, the changes will only be applied after re-opening the project. Reloading the project is not sufficient.
Selecting a build type from command line¶
To select the build type when building the application from command line, specify the build type by adding the following parameter to the west build command:
-- -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=selected_build_type
For example, you can replace the selected_build_type variable to build the ZRelease firmware for PCA20053 by running the following command in the project directory:
west build -b thingy53_nrf5340_cpuapp -d build_thingy53_nrf5340_cpuapp -- -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ZRelease
The build_thingy53_nrf5340_cpuapp parameter specifies the output directory for the build files.
Note
If the selected board does not support the selected build type, the build is interrupted.
For example, if the ZDebugWithShell build type is not supported by the selected board, the following notification appears:
Configuration file for build type ZDebugWithShell is missing.
Testing¶
Note
The testing procedure assumes you are using the mobile Matter controller application. You can also obtain the measurement values using the PC command-line-based Matter controller and invoking the read commands manually. To see how to send read commands from the PC Matter controller, read the Working with Python CHIP Controller guide in the Matter documentation.
After programming the application, perform the following steps to test the Matter weather station application on the Thingy:53 with the mobile Matter controller application:
Turn on the Thingy:53. The application starts in an unprovisioned state. The advertising over Bluetooth LE and DFU start automatically, and LED 1 starts blinking blue (short flash on).
Commission the device into a Thread network by following the guides linked on the Configuring Matter development environment page for the mobile Matter controller. As part of this procedure, you will complete the following steps:
Configure Thread Border Router.
Build and install the mobile Matter controller.
Commission the device.
Send Matter commands.
During the commissioning procedure, LED 1 of the Matter device starts blinking blue (rapid even flashing). This indicates that the device is connected over Bluetooth LE, but does not yet have full Thread network connectivity.
Note
To start commissioning, the controller must get the commissioning information from the Matter accessory device. The data payload, which includes the device discriminator and setup PIN code, is encoded and shared using an NFC tag. When using the debug configuration, you can also get this type of information from the USB interface logs.
Once the commissioning is complete and the device has full Thread connectivity, LED 1 starts blinking purple (short flash on).
Read sensor measurements in Android CHIPTool:
In the Android CHIPTool application main menu, tap the SENSOR CLUSTERS button to open the sensor measurements section. This section contains text boxes to enter Device ID and Endpoint ID, a drop-down menu with available measurements and two buttons, READ and WATCH.

Sensor cluster section selection¶
On this image, Device ID has the value
5and Endpoint ID has the value1.Select one of the available measurement types from the drop-down menu.
Enter one of the following values for Endpoint ID, depending on the selected measurement type:
1 - Temperature measurement
2 - Relative humidity measurement
3 - Air pressure measurement
Tap the READ button to read and display the single measurement value.
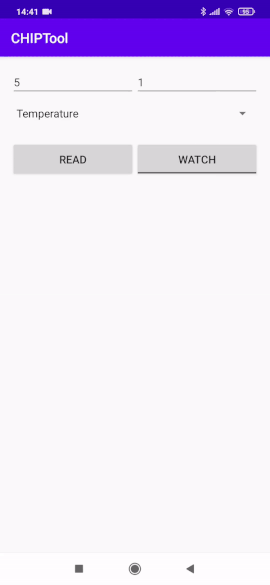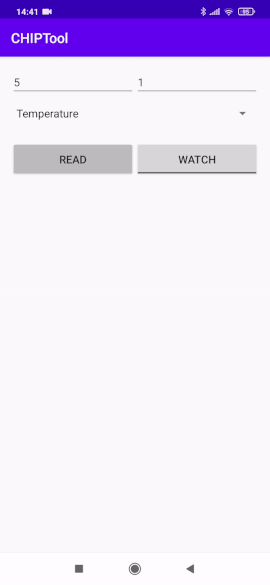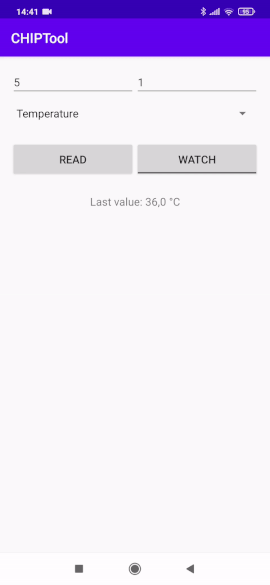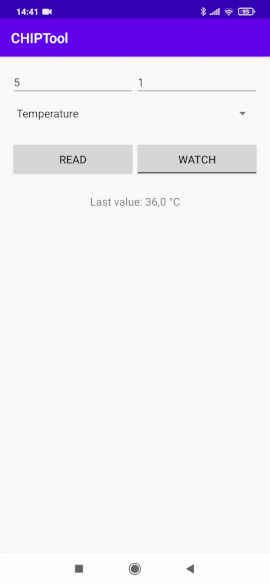
Single temperature measurement read¶
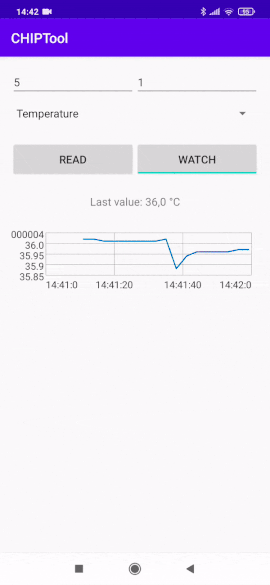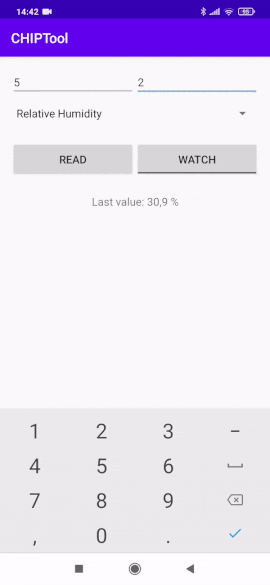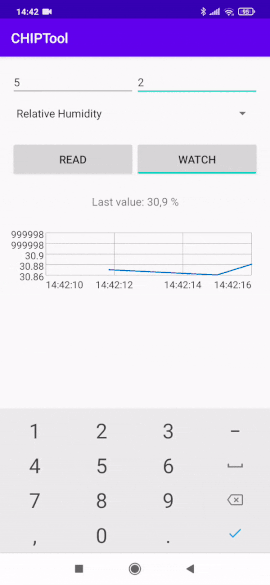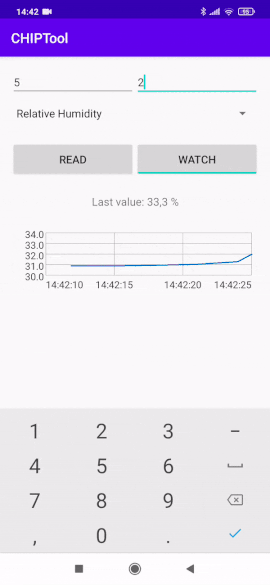
Tap the WATCH button to start watching measurement changes in a continuous way and display values on a chart.
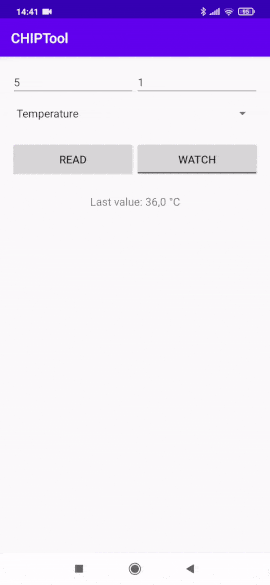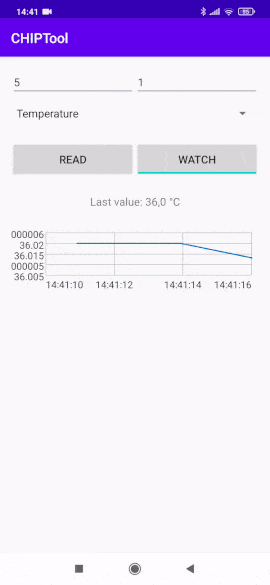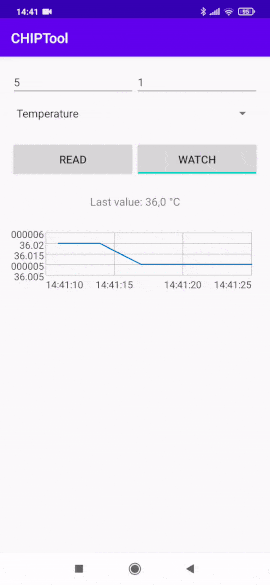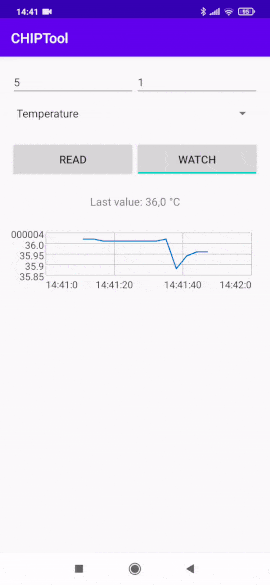
Continuous temperature measurement watch¶
The vertical axis represents the measurement values and the horizontal axis represents the current time.
Change the displayed measurement by selecting a different measurement type from the drop-down list and entering the corresponding Endpoint ID value.
Relative humidity measurement type selection¶
Updating the device firmware¶
Note
Device Firmware Upgrade feature is under development and currently it is possible to update only the application core image. Network core image update is not yet available.
To update the device firmware, complete the steps listed for the selected method in the Performing Device Firmware Upgrade in the nRF Connect examples tutorial in the Matter documentation.
Dependencies¶
This application uses the Matter library, which includes the nRF Connect SDK platform integration layer:
In addition, the application uses the following nRF Connect SDK components:
The application depends on the following Zephyr libraries: