6. Hardware Abstraction Layer¶
- Organization
Arm Limited
- Contact
- API Version
0.9
6.1. Introduction¶
TF-M HAL abstracts the hardware-oriented and platform specific operations on the SPE side and provides a set of APIs to the upper layers such as SPM, RoT Service. The HAL aims to cover the platform different aspects whereas common architecturally defined aspects are done generically within the common SPE. In some cases, although the operations are defined architecturally, it may not be possible to generalize implementations because lots of information is only known to platforms. It is more efficient to define a HAL API for those architectural operations as well.
Note
TBSA-M provides the hardware requirements for security purposes. TF-M HAL tries to reference TBSA-M recommendations in the interfaces from the software perspective only. Please reference TBSA-M for your security hardware design.
6.1.1. Design Goals¶
TF-M HAL is designed to simplify the integration efforts on different platforms.
TF-M HAL is designed to make it easy to use the hardware and develop the SPM and RoT Service which need to access the devices.
TF-M HAL is designed to make the structure clearer and let the TF-M mainly focus on PSA implementation.
6.2. Overview¶
This section provides an overview of the abstraction layer structure.
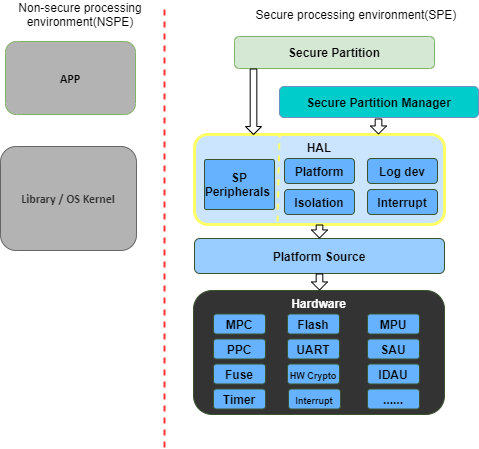
Here lists a minimal set of necessary functionalities:
Isolation API: Provides the necessary isolation functionalities required by the PSA-FF-M and TBSA-M, and provides APIs to SPM to check the permissions of memory access.
Platform API: Provides the platform initialization, platform-specific memory information, system reset, etc.
Log dev API: Provides the log system functions.
Interrupt API: Provides the interrupt functions.
Note
There is a non-secure HAL that focuses on the mailbox operation API for Dual-core topology. For more information about it, please refer to Mailbox Design in TF-M on Dual-core System.
The minimal set of TF-M HAL is sufficient for Secure Partitions by using customized peripheral interfaces. To provide easier portability for the Secure Partitions, a Secure Partition HAL is provided in this design too.
The debug mechanisms give the external entity the corresponding right to access the system assets. TF-M ensures that the external entity is permitted access to those assets. Currently, TF-M only needs the debug authentication. The whole debug mechanism and related HAL will be enhanced in the future. Please refer to the Debug authentication settings section for more detail.
6.3. Design Principles¶
As TF-M runs on resource-constrained devices, the HAL tries to avoid multiple level abstractions which cost more resources.
Part of the HAL interfaces does not focus on exact hardware operations such as power on/off or PIN manipulation. Instead, the HAL abstracts higher-level interfaces to reserve the implementation flexibility for the platform vendors.
The TF-M HAL should be easy to deprecate APIs and provide compatibilities. Any API incompatibility should be detected during building.
TF-M relies on the HAL APIs to be implemented correctly and trusts the HAL APIs. TFM can provide assertions to detect common programming errors but essentially no further extensive checks will be provided.
6.4. Source Files¶
This section describes the source file of the TF-M HAL, including the header and c files.
6.4.1. tfm_hal_defs.h¶
This header file contains the definitions of common macros and types used by all HAL APIs. Please refer to Status Codes for detailed definitions.
6.4.2. tfm_hal_[module].[h/c]¶
All other headers and c files are classified by the modules, such as isolation, platform, interrupt, devices, etc.
Note
There are common files in the platform folder include the implemented HAL APIs. The platform vendors can use them directly but need to implement all the sub APIs.
6.5. Status Codes¶
These are common status and error codes for all HAL APIs.
6.5.1. Types¶
6.5.1.1. tfm_hal_status_t¶
This is a status code to be used as the return type of HAL APIs.
enum tfm_hal_status_t {
TFM_HAL_ERROR_MEM_FAULT = SCHAR_MIN,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_MAX_VALUE,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_BAD_STATE,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_INIT,
TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC,
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS = 0
};
6.5.2. Error Codes¶
Negative values indicate an error. Zero and positive values indicate success.
Here is the general list. The detailed usages for each error code are described in the API introduction sections.
6.5.2.1. TFM_HAL_SUCCESS¶
Status code to indicate general success.
6.5.2.2. TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC¶
Status code to indicate an error that does not correspond to any defined failure cause.
6.5.2.3. TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_INIT¶
Status code to indicate that the module is not initialed.
6.5.2.4. TFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT¶
Status code to indicate that the input is invalid.
6.5.2.5. TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED¶
Status code to indicate that the requested operation or a parameter is not supported.
6.5.2.6. TFM_HAL_ERROR_BAD_STATE¶
Status code to indicate that the requested action cannot be performed in the current state.
6.5.2.7. TFM_HAL_ERROR_MAX_VALUE¶
Status code to indicate that the current number has got the max value.
6.5.2.8. TFM_HAL_ERROR_MEM_FAULT¶
Status code to indicate that the memory check failed.
6.6. API Definition for TF-M SPM¶
This section describes the APIs defined for TF-M SPM.
6.6.1. Platform API¶
The platform API is a higher-level abstraction layer of the platform, other than a dedicated API set for the special hardware devices.
6.6.1.1. APIs¶
6.6.1.1.1. tfm_hal_platform_init()¶
Prototype
enum tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_platform_init(void)
Description
This API performs the platform-specific initialization.
This API is called after architecture and platform common initialization has finished during system early startup.
Parameter
void- None.
Return Values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- Init success.TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC- Generic errors.
6.6.1.1.2. tfm_hal_system_reset()¶
Prototype
void tfm_hal_system_reset(void)
Description
This API performs a system reset.
The platform can uninitialize some resources before reset.
Parameter
void- None
Return Values
void- None
Note
This API should not return.
6.6.2. Isolation API¶
The PSA-FF-M defines three isolation levels and a memory access rule to provide diverse levels of securitiy. The isolation API provides the functions to implement these requirements.
6.6.2.1. Memory Access Attributes¶
The memory access attributes are encoded as bit fields, you can logic OR them to
have a combination of the atrributes, for example
TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_UNPRIVILEGED | TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_READABLE is unprivileged
readable. The data type is uint32_t.
6.6.2.1.1. TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_EXECUTABLE¶
The memory is executable.
#define TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_EXECUTABLE (1UL << 0)
6.6.2.1.2. TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_READABLE¶
The memory is readable.
#define TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_READABLE (1UL << 1)
6.6.2.1.3. TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_WRITABLE¶
The memory is writable.
#define TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_WRITABLE (1UL << 2)
6.6.2.1.4. TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_UNPRIVILEGED¶
The memory is unprivileged mode accessible.
#define TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_UNPRIVILEGED (1UL << 3)
6.6.2.1.5. TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_DEVICE¶
The memory is a MMIO device.
#define TFM_HAL_MEM_ATTR_DEVICE (1UL << 4)
6.6.2.2. APIs¶
6.6.2.2.1. tfm_hal_set_up_static_boundaries()¶
Prototype
tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_set_up_static_boundaries(void)
Description
This API sets up the static isolation boundaries which are constant throughout the runtime of the system.
The boundaries include:
The PSA RoT isolation boundary between the PSA Root of Trust and the Application Root of Trust which is for isolation level 2 and 3 only.
Please refer to the PSA-FF-M for the definitions of the isolation boundaries.
Return Values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- the isolation boundaries have been set up.TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC- failed to set up the isolation boundaries.
6.6.2.2.2. tfm_hal_mpu_update_partition_boundary¶
Prototype
enum tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_mpu_update_partition_boundary(uintptr_t start,
uintptr_t end);
Description
This API updates the partition isolation boundary for isolation level 3. Inside the partition isolation boundary is the private data of the running Secure Partition. This boundary is updated dynamically when SPM switches Partitions in isolation level 3.
The access permissions of the boundary is all privileged mode read-write.
Platforms decide which MPU region the paritition boundary uses.
Parameter
start- start address of the partition boundary.end- end address of the partition boundary.
Return Values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- the isolation boundary has been set up.TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC- failed to set upthe isolation boundary.
Note
This API is only for platforms using MPU as isolation hardwares. A generic API for all platforms will be introduced in future versions.
6.6.2.2.3. tfm_hal_memory_has_access()¶
Prototype
tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_memory_has_access(const uintptr_t base,
size_t size,
uint32_t attr)
Description
This API checks if the memory region defined by base and size has the
given access atrributes - attr.
The Attributes include NSPE access, privileged mode, and read-write permissions.
Parameter
base- The base address of the region.size- The size of the region.attr- The Memory Access Attributes.
Return Values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- The memory region has the access permissions.TFM_HAL_ERROR_MEM_FAULT- The memory region does not have the access permissions.TFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT- Invalid inputs.TFM_HAL_ERROR_GENERIC- An error occurred.
6.6.3. Log API¶
The log API is used by the TF-M log system. The log device could be uart, memory, usb, etc.
6.6.3.1. APIs¶
6.6.3.1.1. tfm_hal_output_partition_log()¶
Prototype
int32_t tfm_hal_output_partition_log(const unsigned char *str, uint32_t len)
Description
This API is called by Secure Partition to output logs.
Parameter
str- The string to output.len- Length of the string in bytes.
Return Values
Positive values - Number of bytes output.
TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_INIT- The log device has not been initialized.TFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT- Invalid inputs whenstrisNULLorlenis zero.
Note
None.
6.6.3.1.2. tfm_hal_output_spm_log()¶
Prototype
int32_t tfm_hal_output_spm_log(const unsigned char *str, uint32_t len)
Description
This API is called by SPM to output logs.
Parameter
str- The string to output.len- Length of the string in bytes.
Return Values
Positive numbers - Number of bytes output.
TFM_HAL_ERROR_NOT_INIT- The log device has not been initialized.TFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT- Invalid inputs whenstrisNULLorlenis zero.
Note
Please check TF-M log system for more information.
6.7. API Definition for Secure Partitions¶
The Secure Partition (SP) HAL mainly focuses on two parts:
Peripheral devices. The peripherals accessed by the TF-M default Secure Partitions.
Secure Partition abstraction support. The Secure Partition data that must be provided by the platform.
The Secure Partition abstraction support will be introduced in the peripheral API definition.
6.7.1. ITS and PS flash API¶
There are two kinds of flash:
Internal flash. Accessed by the PSA Internal Trusted Storage (ITS) service.
External flash. Accessed by the PSA Protected Storage (PS) service.
The ITS HAL for the internal flash device is defined in the tfm_hal_its.h
header and the PS HAL in the tfm_hal_ps.h header.
6.7.1.1. Macros¶
6.7.1.1.1. Internal Trusted Storage¶
6.7.1.1.1.1. TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_DRIVER¶
Defines the identifier of the CMSIS Flash ARM_DRIVER_FLASH object to use for ITS. It must have been allocated by the platform and will be declared extern in the HAL header.
6.7.1.1.1.2. TFM_HAL_ITS_PROGRAM_UNIT¶
Defines the size of the ITS flash device’s physical program unit (the smallest unit of data that can be individually programmed to flash). It must be equal to TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_DRIVER.GetInfo()->program_unit, but made available at compile time so that filesystem structures can be statically sized.
6.7.1.1.1.3. TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_ADDR¶
Defines the base address of the dedicated flash area for ITS.
6.7.1.1.1.4. TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_SIZE¶
Defines the size of the dedicated flash area for ITS in bytes.
6.7.1.1.1.5. TFM_HAL_ITS_SECTORS_PER_BLOCK¶
Defines the number of contiguous physical flash erase sectors that form a logical filesystem erase block.
6.7.1.1.2. Protected Storage¶
6.7.1.1.2.1. TFM_HAL_PS_FLASH_DRIVER¶
Defines the identifier of the CMSIS Flash ARM_DRIVER_FLASH object to use for PS. It must have been allocated by the platform and will be declared extern in the HAL header.
6.7.1.1.2.2. TFM_HAL_PS_PROGRAM_UNIT¶
Defines the size of the PS flash device’s physical program unit (the smallest unit of data that can be individually programmed to flash). It must be equal to TFM_HAL_PS_FLASH_DRIVER.GetInfo()->program_unit, but made available at compile time so that filesystem structures can be statically sized.
6.7.1.1.2.3. TFM_HAL_PS_FLASH_AREA_ADDR¶
Defines the base address of the dedicated flash area for PS.
6.7.1.1.2.4. TFM_HAL_PS_FLASH_AREA_SIZE¶
Defines the size of the dedicated flash area for PS in bytes.
6.7.1.1.2.5. TFM_HAL_PS_SECTORS_PER_BLOCK¶
Defines the number of contiguous physical flash erase sectors that form a logical filesystem erase block.
6.7.1.2. Optional definitions¶
The TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_ADDR, TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_SIZE and
TFM_HAL_ITS_SECTORS_PER_BLOCK definitions are optional. If not defined, the
platform must implement tfm_hal_its_fs_info() instead.
Equivalently, tfm_hal_its_ps_info() must be implemented by the platform if
TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_ADDR, TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_AREA_SIZE or
TFM_HAL_ITS_SECTORS_PER_BLOCK is not defined.
6.7.1.3. Objects¶
6.7.1.3.1. ARM_DRIVER_FLASH¶
The ITS and PS HAL headers each expose a CMSIS Flash Driver instance.
extern ARM_DRIVER_FLASH TFM_HAL_ITS_FLASH_DRIVER
extern ARM_DRIVER_FLASH TFM_HAL_PS_FLASH_DRIVER
The CMSIS Flash Driver provides the flash primitives ReadData(), ProgramData() and EraseSector() as well as GetInfo() to access flash device properties such as the sector size.
6.7.1.4. Types¶
6.7.1.4.1. tfm_hal_its_fs_info_t¶
Struct containing information required from the platform at runtime to configure the ITS filesystem.
struct tfm_hal_its_fs_info_t {
uint32_t flash_area_addr;
size_t flash_area_size;
uint8_t sectors_per_block;
};
Each attribute is described below:
flash_area_addr- Location of the block of flash to use for ITS
flash_area_size- Number of bytes of flash to use for ITS
sectors_per_block- Number of erase sectors per logical FS block
6.7.1.4.2. tfm_hal_ps_fs_info_t¶
Struct containing information required from the platform at runtime to configure the PS filesystem.
struct tfm_hal_ps_fs_info_t {
uint32_t flash_area_addr;
size_t flash_area_size;
uint8_t sectors_per_block;
};
Each attribute is described below:
flash_area_addr- Location of the block of flash to use for PS
flash_area_size- Number of bytes of flash to use for PS
sectors_per_block- Number of erase sectors per logical FS block
6.7.1.5. Functions¶
6.7.1.5.1. tfm_hal_its_fs_info()¶
Prototype
enum tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_its_fs_info(struct tfm_hal_its_fs_info_t *fs_info);
Description
Retrieves the filesystem configuration parameters for ITS.
Parameter
fs_info- Filesystem config information
Return values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- The operation completed successfullyTFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT- Invalid parameter
Note
This function should ensure that the values returned do not result in a security compromise. The block of flash supplied must meet the security requirements of Internal Trusted Storage.
6.7.1.5.2. tfm_hal_ps_fs_info()¶
Prototype
enum tfm_hal_status_t tfm_hal_ps_fs_info(struct tfm_hal_ps_fs_info_t *fs_info);
Description
Retrieves the filesystem configuration parameters for PS.
Parameter
fs_info- Filesystem config information
Return values
TFM_HAL_SUCCESS- The operation completed successfullyTFM_HAL_ERROR_INVALID_INPUT- Invalid parameter
Note
This function should ensure that the values returned do not result in a security compromise.
Copyright (c) 2020-2021, Arm Limited. All rights reserved.