|
nRF5 IoT SDK
v0.9.0
|
|
nRF5 IoT SDK
v0.9.0
|
Commissioning a Bluetooth Smart node to a 6LoWPAN network is integrated into all example applications in the IoT SDK. This section describes how to enable commissioning in an example application.
Choose one of the projects inside the IoT SDK, for example CoAP server.
In order to activate commissioning mode, the following symbol has to be defined for the C preprocessor:
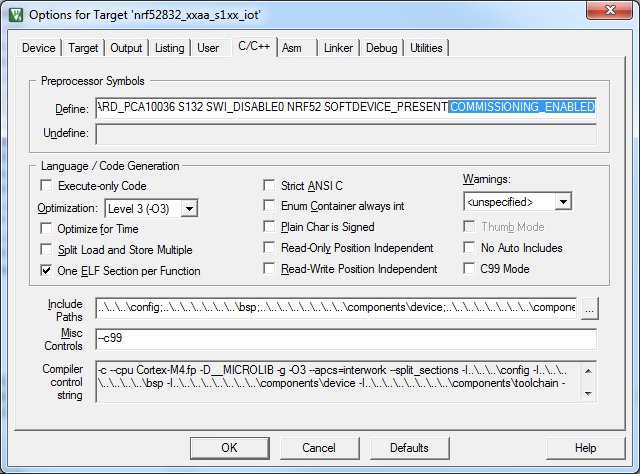
To define the COMMISSIONING_ENABLED symbol in Keil µVision projects, open the Options for Target dialog and select the C/C++ tab. In the Define field, add COMMISSIONING_ENABLED to the end of the define.
To define the COMMISSIONING_ENABLED symbol for the ARM GCC compiler, add the following line in the C flags section of the Makefile:
Now compile the example and flash it to the nRF52 Developer Kit.
Once commissioning is enabled, some of the LEDs (LED 3 and LED 4 in most cases) are used to indicate that the node is in Identity mode. Depending on the application, Button 3 or Button 4 is used to erase commissioning-related settings from persistent storage.
The Linux based daemon has been prepared for the edge router. The current version of the daemon was tested on OpenWRT targets (Chaos Calmer 15.05) and Ubuntu (Linux Kernel 3.18+), and the documentation describes usage on these systems.
The first step is to build and run the bluetooth_6lowpand daemon.
After the daemon is successfully built, start it up and test if the help window is visible.
On an OpenWRT platform with Wi-Fi enabled, the Wi-Fi network configuration can be read and reused by the daemon. In this example, however, the SSID and passphrase will be manually added.
Run the following code:
/etc/init.d/bluetooth_6owpand start.Prepare the Trusted Third Party by installing and running the nRF IoT Joiner Android application.
Configure Wi-Fi manually with the credentials given to the router.
The next step is to find the already advertising nRF device, which should be visible as NodeCFG in the main dashboard of the mobile application. Select the proper device and configure it with the default parameters (10 seconds delay, 20 seconds of timeout). After the configured delay, the node should connect to the network automatically.
Test if the pre-flashed application works properly, for example by pinging the commissioned device.