TSC Project Roles¶
Main Roles¶
TSC projects generally will involve Maintainers, Collaborators, and Contributors:
Maintainer: lead Collaborators on an area identified by the TSC (e.g. Architecture, code subsystems, etc.). Maintainers shall also serve as the area’s representative on the TSC as needed. Maintainers may become voting members of the TSC under the guidelines stated in the project Charter.
Collaborator: A highly involved Contributor in one or more areas. May become a Maintainer with approval of existing TSC voting members.
Contributor: anyone in the community that contributes code or documentation to the project. Contributors may become Collaborators by approval of the existing Collaborators and Maintainers of the particular code base areas or subsystems.
Contributor¶
A Contributor is a developer who wishes to contribute to the project, at any level. Contributors who show dedication and skill are rewarded with additional rights and responsibilities.
Contributors are granted the following rights and responsibilities:
Right to contribute code, documentation, translations, artwork, etc.
Right to report defects (bugs) and suggestions for enhancement.
Right to participate in the process of reviewing contributions by others.
Right to initiate and participate in discussions in any communication methods.
Right to approach any member of the community with matters they believe to be important.
Right to participate in the feature development process.
Responsibility to abide by decisions, once made. They are welcome to provide new, relevant information to reopen decisions.
Responsibility for issues and bugs introduced by one’s own contributions.
Responsibility to respect the rules of the community.
Responsibility to provide constructive advice whenever participating in discussions and in the review of contributions.
Responsibility to follow the project’s code of conduct (https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr/blob/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md)
Collaborator¶
A Collaborator is a Contributor who is also responsible for the maintenance of Zephyr source code. Their opinions weigh more when decisions are made, in a fully meritocratic fashion.
Collaborators have the following rights and responsibilities, in addition to those listed for Contributors:
Right to set goals for the short and medium terms for the project being maintained, alongside the Maintainer.
Responsibility to participate in the feature development process.
Responsibility to review relevant code changes within reasonable time.
Responsibility to ensure the quality of the code to expected levels.
Responsibility to participate in community discussions.
Responsibility to mentor new contributors when appropriate
Responsibility to participate in the quality verification and release process, when those happen.
Maintainer¶
A Maintainer is a Collaborator who is also responsible for knowing, directing and anticipating the needs of a given zephyr source code area.
Maintainers have the following rights and responsibilities, in addition to those listed for Contributors and Collaborators:
Right to set the overall architecture of the relevant subsystems or areas of involvement.
Right to make decisions in the relevant subsystems or areas of involvement, in conjunction with the collaborators.
Responsibility to convey the direction of the relevant subsystem or areas to the TSC
Responsibility to ensure all contributions of the project have been reviewed within reasonable time.
Responsibility to enforce the code of conduct.
Role Retirement¶
Individuals elected to the following Project roles, including, Maintainer, Release Engineering Team member, Release Manager, but are no longer engaged in the project as described by the rights and responsibilities of that role, may be requested by the TSC to retire from the role they are elected.
Such a request needs to be raised as a motion in the TSC and be approved by the TSC voting members. By approval of the TSC the individual is considered to be retired from the role they have been elected.
The above applies to elected TSC Project roles that may be defined in addition.
Teams and Supporting Activities¶
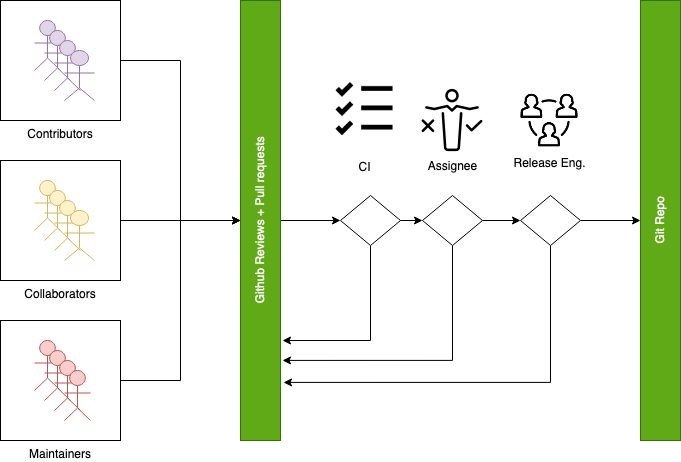
Assignee¶
An Assignee is one of the maintainers of a subsystem or code being changed. Assignees are set either automatically based on the code being changed or set by the other Maintainers, the Release Engineering team can set an assignee when the latter is not possible.
Right to dismiss stale reviews and seek reviews from additional maintainers, developers and contributors
Right to block pull requests from being merged
Responsibility to re-assign a pull request if they are the original submitter of the code
Responsibility to drive the pull request to a mergeable state
Solicit approvals from maintainers of the subsystems affected
Responsibility to drive the escalation process
Release Engineering Team¶
A team of active Maintainers involved in multiple areas.
The members of the Release Engineering team are expected to fill the Release Manager role based on a defined cadence and selection process.
The cadence and selection process are defined by the Release Engineering team and are approved by the TSC.
The team reports directly into the TSC.
Release Engineering team has the following rights and responsibilities:
Right to merge code changes to the zephyr tree following the project rules.
Right to revert any changes that have broken the code base
Right to close any stale changes after <N> months of no activity
Responsibility to take directions from the TSC and follow them.
Responsibility to coordinate code merges with maintainers.
Responsibility to merge all contributions regardless of their origin and area if they have been approved by the respective maintainers and follow the merge criteria of a change.
Responsibility to keep the Zephyr code base in a working and passing state (as per CI)
Joining the Release Engineering team
Maintainers highly involved in the project may be nominated by a TSC voting member to join the Release Engineering team. Nominees may become members of the team by approval of the existing TSC voting members.
To ensure a functional Release Engineering team the TSC shall periodically review the team’s followed processes, the appropriate size, and the membership composition (ensure, for example, that team members are geographically distributed across multiple locations and time-zones).
Release Activity¶
MAINTAINERS File¶
Generic guidelines for deciding and filling in the Maintainers’ list
The MAINTAINERS file shall coexist with the CODEOWNERS file. MAINTAINERS file is used to set assignees, CODEOWNERS file is used for more granularity and to add reviewers down to the file level. CODEOWNERS file entries do not signify maintainership.
We should keep the granularity of code maintainership at a manageable level
We should be looking for maintainers for areas of code that are orphaned (i.e. without an explicit maintainer)
Un-maintained areas should be indicated clearly in the MAINTAINERS file
All submitted pull-requests should have an assignee
We Introduce an area/subsystem hierarchy to address the above point
Parent-area maintainer should be acting as default substitute/fallback assignee for un-maintained sub-areas
Area maintainer gets precedence over parent-area maintainer
Pull-requests may be re-assigned if this is needed or more appropriate
Re-assigned by original assignee (see “Assignee” slide)
Updates to the MAINTAINERS file should be in a standalone PRs
The MAINTAINERS file itself shall have a maintainer
Architectures, core components, sub-systems, samples, tests
Each area shall have an explicit maintainer
Boards (incl relevant samples, tests), SoCs (incl DTS) * May have a maintainer, shall have a higher-level platform maintainer
Drivers
Shall have a driver-area (and API) maintainer
Could have individual driver implementation maintainers but preferably collaborator/contributors
In the above case, platform-specific PRs may be re-assigned to respective collaborator/contributor of driver implementation
Merge Criteria¶
All continuous integration checks have passed
Codeowners
Device Tree
Documentation
Gitlint
Identity/Emails
Kconfig
License
Checkpatch (Coding Style)
Pylint
Sanitycheck + Other Unit tests
Simulated Bluetooth Tests
Planned
Footprint
Code coverage
Coding Guidelines
Static Analysis (Coverity)
Documentation coverage (APIs)
PR template with checklist
Minimal of 2 approvals
A collaborator from the same subsystem.
Alternately another maintainer of another subsystem
Approval by the assignee
A minimum review period of 2 days, 4 hours for trivial changes (see Give reviewers time to review before code merge). Hotfixes can be merged at any time after CI passes.
All required checks are passing
Escalation Process¶
Contributors may object to change requests or decisions made by Maintainers.
Process
Resolve in the PR among assignee, maintainers and reviewer
Assignee to act as moderator if applicable
Optionally resolve in the dev review meeting with more Maintainers and project stakeholders
The involved parties and the Assignee to be present when the (escalated) issue is discussed
TSC: Assignees can escalate to the TSC voting members and get a binding resolution in the TSC.
Assignee to ensure the resolution of the escalation is reflected in the PR review.
Release Manager¶
A Maintainer responsible for driving a specific release to completion following the milestones and the roadmap of the project for this specific release.
TSC has to approve a release manager.
A Release Manager is a member of the Release Engineering team and has the rights and responsibilities of that team in addition to the following:
Right to manage and coordinate all code merges after the code freeze milestone (M3, see program management overview.)
Responsibility to drive and coordinate the triaging process for the release
Responsibility to create the release notes of the release
Responsibility to notify all stakeholders of the project, including the community at large about the status of the release in a timely manner.
Responsibility to coordinate with QA and validation and verify changes either directly or through QA before major changes and major milestones.